Methods of Preparations of Carboxylic Acids
Methods of Preparations of Carboxylic Acids: Overview
This topic explores the reaction involving the preparation of carboxylic acids from different compounds. It also informs about the details of catalysts used in each reaction.
Important Questions on Methods of Preparations of Carboxylic Acids
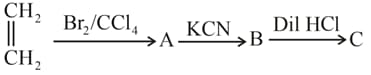
In the above reaction sequence, the product is
The compound in the following reaction scheme:
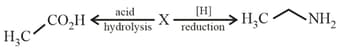 is:
is:
Nitriles are hydrolysed to amides and then to carboxylic acids in the present of which of the following catalyst:
Grignard reagent reacts with carbon dioxide in diethyl ether followed by acid workup to give a carboxylic acid. It is an example of _____ addition reaction.
When Grignard reagent reacts with dry ice an intermediate compound formed called adduct, which on acid hydrolysis gives ethanoic acid.
Which one of the following functional groups undergoes hydrolysis with alkali to yield an acid group?
A hydrocarbon (molecular formula ) on ozonolysis gives ( ) only. Compound ( ) on treatment with magnesium in dry ether gives which on treatment with followed by acidification gives Identify and .
Treatment of compound 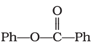 with solution yields
with solution yields
How will you convert bromoethane into ethanoic acid ?
Alkyl halides are converted into nitriles by the action of aqueous or aqueous-alcoholic . The reaction follows mechanism and works best with primary and secondary alkyl halides. Aryl halides are extremely less reactive towards nucleophilic substitutions. Identify the correct procedure for the following conversion.
-Chloroethanol into -hydroxypropanoic acid.
Alkyl halides are converted into nitriles by the action of aqueous or aqueous-alcoholic . The reaction follows mechanism and works best with primary and secondary alkyl halides. Aryl halides are extremely less reactive towards nucleophilic substitutions. Identify the correct procedure for the following conversion.
tert-butyl bromide into -Dimethylpropanoic acid.
Alkyl halides are converted into nitriles by the action of aqueous or aqueous-alcoholic . The reaction follows mechanism and works best with primary and secondary alkyl halides. Aryl halides are extremely less reactive towards nucleophilic substitution. Identify the correct procedure for the following conversion.
-Chlorobutane into -Methylbutanoic acid
Alkyl halide are converted into nitriles by the action of aqueous or aqueous-alcoholic . The reaction follows mechanism and works best with primary and secondary alkyl halides. Aryl halides are extremely less reactive towards nucleophilic substitutions. Identify the correct procedure for the following conversion.
-Nitrochlorobenzene into -Nitrobenzoic acid
Write the structure and IUPAC name of the product formed in following conversion.
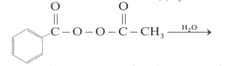
Write the structure and IUPAC name of the product formed in following conversion
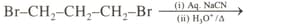
Write the structure and IUPAC name of products formed in the following conversion
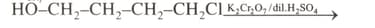
Write the structure and IUPAC name of the products formed in the following conversion
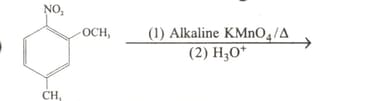
How is butanoic acid is prepared starting from an alkene?
How is butanoic acid is prepared starting from an alkyl halide?
How is butanoic acid is prepared starting from an alcohol?
